Water-soluble CBD has revolutionized the beverage industry, catering to the “Sober Curious Consumer” and wellness enthusiasts seeking functional alternatives to alcohol. As Mile High Labs’ General Manager, Bo Becker, explains, water-soluble CBD provides a unique sensation without the need for alcohol, fueling demand in both the US and international markets. The CBD drinks category is set for rapid expansion, with Brightfield Group forecasting a staggering 40.5% CAGR from 2021-2026, and numerous beverage brands are eager to harness the potential of this groundbreaking water-soluble CBD trend.
One of the biggest challenges with CBD is that it is not inherently water-soluble. This means that it does not dissolve into water, making it more challenging for use in its typical format, within an emerging and growing consumer use occasion: drinks and beverages. To overcome this challenge, manufacturers have developed various techniques to make CBD water-soluble. It is more universally known in the CBD industry as “Water-Soluble”, but in reality, CBD is “Water-Dispersible”, because oil cannot dissolve in water. In this article, we will discuss how CBD is made water-soluble (or dispersible) and why it matters.
What is CBD Water Solubility?
Water-solubility refers to the ability of a substance to be dispersed in water. CBD is an oil. This can create problems when it comes to its bioavailability, or the degree to which it can be absorbed and used by the body, or in how it mixes into or stays in a consistent solution within a beverage. The reason for that is because 60%-70% of the human body is made of water, or is hydrophilic, hence water-soluble compounds are easily absorbed in the body.

When CBD is ingested, it first makes its way into the GI Tract where the body releases enzymes that specialize in breaking down large oil droplets into smaller droplets, until they are small enough to penetrate through the GI Tract membrane and go systemic. Overall, only 5%-10% of ingested CBD oil is absorbed, and the rest (90%-95%) is excreted by the body unchanged. The absorption is 5% if the user is not on a fatty diet and is about 10% if the user has had a fatty meal before ingesting CBD. This is because a fatty diet makes the body produce an elevated amount of enzymes which will help break down CBD oil droplets more efficiently.
Water-Soluble CBD has a much smaller average oil droplet size, which means that it is already small enough to absorb into the body without much help from the enzymes.
What Are the Benefits of Bioavailable CBD

According to Vardan Ter-Antonyan, R&D Manager, at Mile High Labs, CBD is:
- A stable molecule if pH is considered when formulating to avoid oxidative stress.
- Temperature-stable if not exposed to excessive temperatures for extended periods to avoid thermolytic stress.
- Exceptional, in general, when it comes to solubility in oil-based mediums.
CBD has been included in various beverages, as of late, along with other supportive functional ingredients, like turmeric to potentially help reduce exercise induced inflammation; along with magnesium and L-Theanine, to help support a sense of calm; or melatonin and lemon balm to support a healthy night’s sleep. With all these new beverage combinations, it is important that the functional ingredients stay in a stable dispersion or emulsion, as well as allows the consumer to have a pleasant consumption experience through stable and consistent organoleptics (color, taste, smell, and mouthfeel). Water-soluble CBD addresses this issue by allowing the CBD to stay in dispersion and minimize color and clarity concerns more effectively. It is noteworthy that CBD oil by itself is very bitter and the smaller its droplet size the more bitter it becomes, simply because it is more bioavailable. This means optimizing the droplet size to be not too large (to avoid absorption issues), but also not too small (to avoid organoleptic issues).
How is CBD Made Water-Soluble?
There are several methods involving nanotechnology that manufacturers can use to make CBD water-soluble or dispersible. The most common methods involve breaking down the large CBD oil droplets into smaller droplets using the process of ultrasonic cavitation, or high-pressure homogenization. CBD isolate, or distillate, is first dissolved in a carrier oil. This oil phase is then mixed in with the water phase that consists of water and emulsifiers, at a specific elevated temperature. Emulsifiers are molecules that contain a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail (see pictures below).
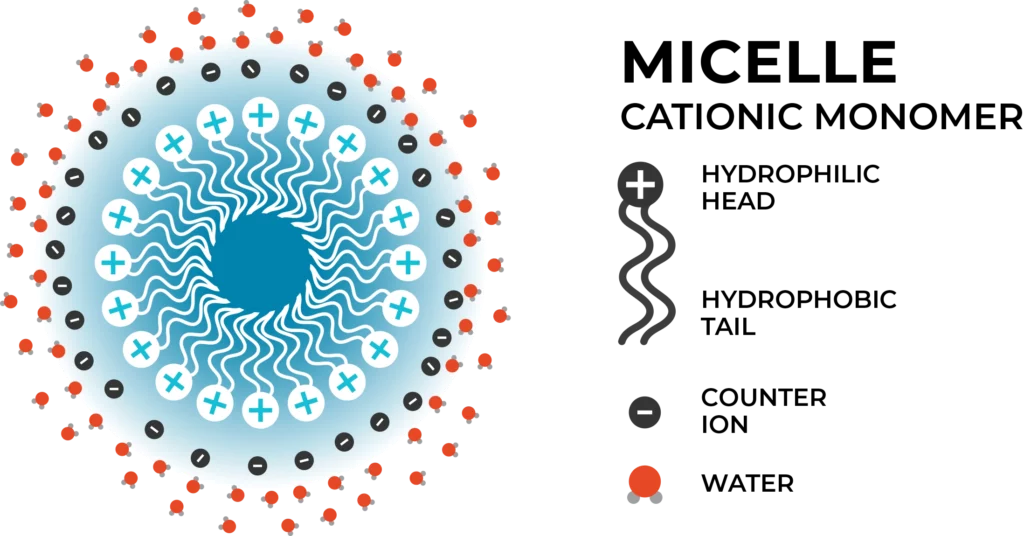
When making oil-in-water emulsions, the emulsifiers self organize into micelles that are organized in such a way that the hydrophobic (water hating) tails of the emulsifiers are pointed towards the oil droplets in the core of the micelle, and hydrophilic (water loving) heads are pointing outwards towards the surrounding water. The smaller the micelles, the smaller the oil droplet in the core, the higher is the bioavailability/absorption of that oil droplet in the body. When oil phase and water phase are mixed together, large 3um-4um micelles start forming. When these large micelles are ultrasonicated using a high frequency ultrasonicator, or homogenized using a high-pressure homogenizer, the large micelles break down into smaller micelles. The smaller the micelles, the more translucent the micro-emulsion is. In science, unless the emulsion has an average droplet size of 100nm or below, it is not called a “Nano emulsion”, however the nano emulsion size range is not well defined, hence some define an emulsion with an average droplet size of <1000nm as a nano emulsion, and some call it a microemulsion.
Mile High Labs’ Technique
Vardan Ter-Antonyan describes some of the unique characteristics of the proprietary CBD water-soluble process, “Creating a stable Oil-in-Water high payload/cannabinoid concentration emulsion is an art that is not easily mastered. The emulsion is self-organizing, but it requires the right type of emulsifiers, in exactly right concentrations, and the emulsion forms under carefully controlled and correct conditions, using the right equipment that outputs the right amount of energy into the system. The higher the concentration of the active oil compound or compounds, the harder it is to achieve a stable emulsion with the smallest possible oil droplet size.”
One of the important parameters in the formulation that must be tightly controlled is the ratio between the %(w/w) (weight per weight) of carrier oil and the %(w/w) cannabinoid used. The larger this ratio, the smaller the oil droplet size, the more stable is the emulsion, and vice versa. The second important parameter is the type of emulsifiers used and the ratio between the emulsifier concentration and the oil concentration in the emulsion matrix. The same rule applies here, the larger the ratio is, the more stable the emulsion is. Here, one must be careful because the higher the active oil payload, the higher the overall oil concentration in the system, which means the harder it is to form a stable emulsion. Mile High Labs has developed a proprietary stable 20% cannabinoid emulsion unmatched by the industry (in CBD, CBG, and CBN), by carefully choosing emulsifiers to have just the right HLB values and critical micelle concentrations to form a stable emulsion at the smallest droplet size possible with the smallest emulsifier concentration possible for a 20% active payload concentration. Being hidden inside the core of the micelles, the cannabinoids are well protected against photolytic and oxidative degradation. Thermal degradation may still occur, but the temperature needed exceeds any possible temperature range that might be encountered since cannabinoids degrade at above 150C, however micelles will start breaking if exposed to extremely high temperatures of 80C and above for a prolonged period of time.
Finally, the type of equipment used in preparation of the emulsion plays a crucial role in making a stable emulsion. Some of the most popular equipment are High Pressure Homogenizers and Microfluidizers. The way this equipment operates is by passing the microemulsion through very small holes, under high pressure, usually around 30,000psi-40,000psi for multiple passes. Every pass through the equipment lowers the oil droplet size and the micelle size increasing the emulsion stability.
Also popular are in-line ultrasonicators that generate a signal that gets translated into vibration of a titanium horn inside the reactor chamber by means of a transducer. Continuously circulating the emulsion into the reactor chamber, the emulsion gets subjected to violent explosions of air bubbles created by continuously expanding and contracting a titanium horn in the chamber. These explosions decrease the micelle size. Depending on the emulsification system and the payload concentration the droplet size can drop as low as 10nm-20nm, and following filtration through 0.1um filter a sterile transparent nano-emulsion can be collected at the end.
Vardan Ter-Antonyan, R&D Manager, Mile High Labs.
Conclusion
CBD has continued to be an emerging trend for use in the beverage category, but its lack of water solubility can limit its effectiveness. Fortunately, there are methods that manufacturers can use to make CBD water-soluble. These methods involve breaking down the CBD oil droplets into smaller droplets by using emulsifiers and specialized equipment to help the active oils mix with water. Doing so does not impact the CBD molecular purity, or stability, it just increases its bioavailability. By increasing the bioavailability of CBD, water-soluble products can offer more consistent and effective results. So, if you are looking to experience the benefits of CBD, be sure to choose water-soluble products that offer improved absorption and bioavailability.
Want to stay ahead of the latest cannabinoid industry trends? Subscribe to our newsletter and never miss a post!




